Exploring the Differences: Color Sanding vs. Traditional Sanding Techniques
Amidst the vast array of sanding techniques, one term often causing confusion is "color sanding." This specialized technique, primarily used in automotive detailing, is distinct from traditional sanding methods and requires a nuanced approach to achieve a flawless finish.
In this comprehensive blog, we aim to demystify the concept of color sanding by exploring its differences from traditional sanding techniques. From understanding the process and benefits to comparing its applications, we delve into the intricacies of color sanding versus traditional sanding.
What is Color Sanding?

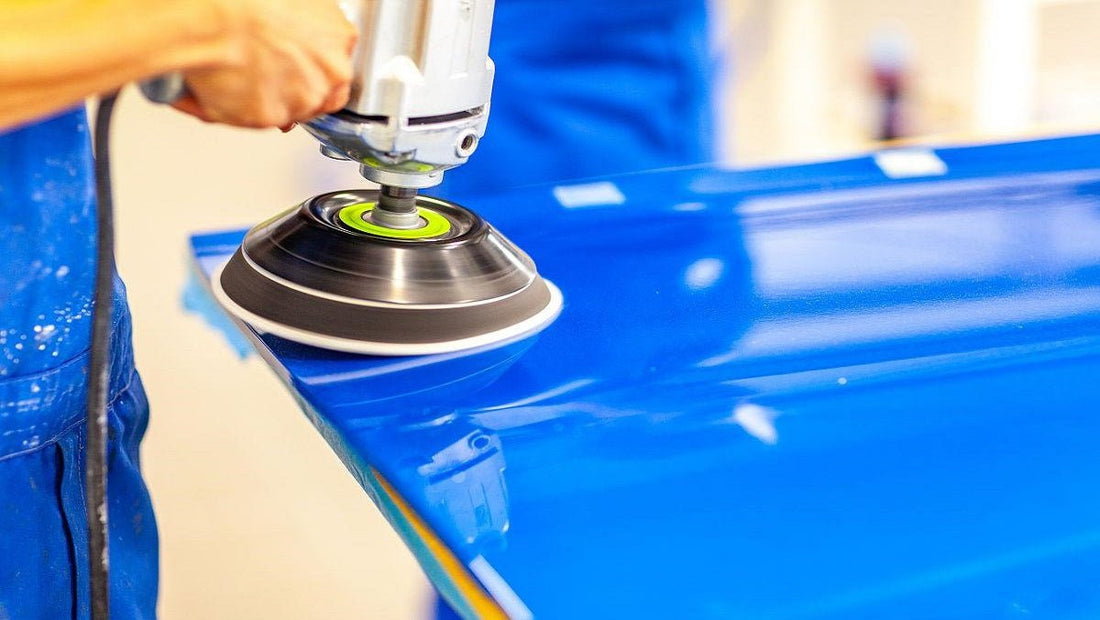
Color sanding is a meticulous technique used to refine and polish automotive paintwork to achieve a flawless, mirror-like finish. Unlike traditional sanding methods, which primarily focus on smoothing surfaces before painting, color sanding is typically performed after the paint has cured to its final hardness.
Traditionally, automotive paints were applied without a clear coat layer, leaving the color coat exposed to the elements. As a result, imperfections in the paint, such as orange peel texture, were common. Color sanding emerged as a method to smooth out these imperfections and enhance the paint's appearance.
With advancements in automotive finishing technology, modern cars are typically coated with a clear layer on top of the color coat. While this clear coat provides protection and depth to the finish, it can still develop imperfections during the application process. Color sanding is employed to eliminate these flaws and achieve a flawless finish.
The Process of Color Sanding
Choosing the Right Grit Sandpaper and Lubricant: Color sanding starts by
choosing the right grit sandpaper, usually falling between the 1000 to 3000 range. Coarser grits tackle initial leveling tasks, while finer ones refine the surface to perfection during the final polishing stage. To ensure seamless sanding, it's vital to use a lubricant that prevents sandpaper from clogging. Water or specialized compounds are commonly relied upon for this purpose. With the correct grit and lubricant, achieving smooth, flawless finishes becomes effortless.
Different Sanding Methods: Color sanding can be performed by hand or using power tools such as orbital sanders. Hand sanding allows for greater control and precision, while orbital sanders expedite the process, especially on larger surfaces. Care must be taken to ensure even pressure and consistent motion to avoid uneven sanding marks.
Progression through Varying Grit Levels: The color sanding process typically involves progressing through multiple grit levels to gradually refine the surface. Beginning with a lower-grit sanding disc (1000 or 1500 grit) effectively eliminates imperfections and evens out the surface. Subsequently, finer grits, reaching up to 3000 or beyond, are employed to polish the surface to a brilliant, high-gloss finish, ensuring a truly impeccable result.
Color sanding is a delicate process that requires patience, skill, and attention to detail. The slightest error in technique or excessive pressure can result in damage to the paintwork, including swirl marks, scratches, or burn-throughs. Therefore, it is crucial to approach color sanding with caution and precision.
Benefits of Color Sanding
Removing Imperfections: Color sanding effectively eliminates various imperfections in the paint, including deep scratches, orange peel texture, and runs. Through the process of leveling the surface, it establishes a seamless canvas, setting the stage for a flawless finish that enhances the overall appearance of the surface.
Achieving a Mirror-like Finish: The ultimate aim of color sanding is to attain a mirror-like, show-quality finish. This is achieved by meticulously refining the surface to a remarkable level of smoothness. Through this process, color sanding elevates the depth and clarity of the paint, culminating in a visually striking appearance that captivates the eye.
Restoring Faded or Oxidized Paint: In addition to enhancing the appearance of new paintwork, color sanding can also be used to restore faded or oxidized paint. By removing the outer layer of damaged paint, color sanding reveals the fresh, vibrant layers underneath, rejuvenating the overall appearance of the vehicle.
Traditional Sanding Techniques

Traditional sanding techniques encompass a variety of methods used to prepare surfaces for painting or finishing. These techniques range from dry sanding to wet sanding, block sanding, and specialized approaches for sanding curved surfaces and specific materials.
Comparison with Color Sanding
Grit Levels and Intended Outcomes: Traditional sanding techniques typically involve the use of coarser grits for initial leveling and finer grits for finishing, while color sanding focuses on progressively finer grits for polishing and refining the surface to a high gloss.
Level of Risk Associated with Damaging the Surface: Traditional sanding techniques carry a lower risk of damaging the surface compared to color sanding, which requires careful control and precision to avoid inadvertently removing too much material or causing swirl marks.
Applications Where Each Technique Might be Preferred: Traditional sanding techniques are suitable for general surface preparation and leveling, while color sanding is preferred for achieving a flawless, show-quality finish on automotive paintwork or other high-gloss surfaces where aesthetic perfection is paramount.
When to Choose Color Sanding vs. Traditional Sanding
Choosing between color sanding and traditional sanding techniques depends on various factors, including the severity of imperfections, desired final finish, skill level, paint type, safety considerations, and potential for mistakes. Here's a decision-making guide to help you determine which technique is most appropriate for your specific situation:
Severity of Imperfections and Desired Final Finish:
Color Sanding: If you're dealing with moderate to severe imperfections like deep scratches, orange peel texture, or runs in the paint, and you desire a flawless, show-quality finish, color sanding is the preferred option. It allows for meticulous refinement and polishing of the surface to achieve a mirror-like shine.
Traditional Sanding: For minor imperfections or surface preparation tasks where a high-gloss finish isn't necessary, traditional sanding techniques may suffice. They are suitable for general leveling and smoothing of surfaces before painting or finishing.
Skill Level and Experience with Sanding Techniques:
Color Sanding: Color sanding requires a higher level of skill and precision compared to traditional sanding techniques due to the delicate nature of the process and the risk of damaging the surface. It's best suited for experienced individuals who are familiar with proper sanding techniques and have a steady hand.
Traditional Sanding: Traditional sanding techniques, particularly dry sanding with coarse grits, may be more forgiving for beginners or those with limited experience. However, attention to detail and proper technique are still essential to avoid mistakes and achieve satisfactory results.
Paint Type and Material Being Sanded:
Color Sanding: Color sanding is most commonly used on automotive paintwork with modern clear-coated finishes. It's also suitable for other high-gloss surfaces like fiberglass or gel coat. However, it may not be ideal for all types of paints or materials, especially those that are sensitive to water or abrasion.
Traditional Sanding: Traditional sanding techniques can be applied to a wide range of materials, including wood, metal, plastic, and drywall. They are versatile and adaptable to different surface types and paint systems.
Safety Considerations and Potential for Mistakes:
Color Sanding: Due to the risk of damaging the paintwork and the meticulous nature of the process, color sanding requires careful attention to safety precautions and technique. Mistakes such as applying too much pressure or using the wrong grit can result in irreversible damage to the surface.
Traditional Sanding: While traditional sanding techniques carry a lower risk of damaging the surface compared to color sanding, safety considerations such as wearing appropriate protective gear and minimizing dust exposure are still important to prevent injury and ensure a satisfactory outcome.
Conclusion
Throughout this guide, we've explored the intricacies of color sanding and its significance in achieving a flawless automotive finish. Don't be afraid to try different sanding methods, experiment with various grits of sandpaper, and hone your skills through trial and error. By continuously practicing and learning from your experiences, you'll develop the expertise and confidence needed to tackle even the most challenging color sanding tasks.
Buy Factory-Direct Fastplus Abrasives
Want to purchase high-quality, factory-direct sanding discs, sanding sheet rolls, and film abrasive discs for automotive applications? Try Fastplus Abrasives today and place your orders online!